

Carotid Artery Stenting is a minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to treat carotid artery blockages, which can restrict the flow of blood to the brain and increase the risk of stroke. The procedure involves placing a carotid stent in the narrowed or blocked carotid artery to improve blood flow and prevent future strokes.
Dr Akhil Monga, a renowned interventional neuroradiologist in Mohali, specialises in Carotid Artery Stenting to provide patients with safer, more effective stroke prevention and treatment options.
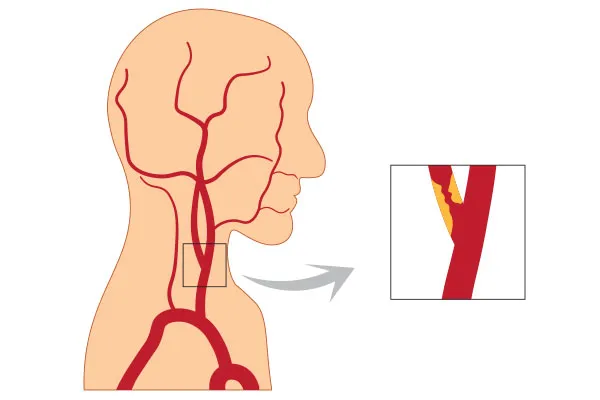
The Carotid Artery Stenting procedure is performed through angiography, where a catheter is introduced into the femoral artery via a small incision. The catheter is navigated up to the carotid artery where the blockage or narrowing is present.
This short procedure typically takes 1-2 hours and is minimally invasive, in nature providing a safer alternative to traditional carotid artery surgery.
Carotid Artery Stenting offers several benefits for patients with severe carotid artery blockages:
After the stenting procedure, patients may be required to:
While carotid stenting is a safe and effective procedure, it is not without risks. Potential complications may include:
Certain factors may increase the risk of complications, such as high blood pressure, poor kidney function, irregular heartbeat, or advanced age. Dr. Akhil Monga will evaluate your health to determine if Carotid Artery Stenting is the best option for you.

Dr. Akhil Monga is an expert in Carotid Artery Stenting, providing patients with advanced care to treat and prevent strokes. With extensive experience and a commitment to patient safety, Dr. Monga ensures that every procedure is performed with precision and care, helping you achieve the best possible outcome.
For expert Carotid Artery Stenting in Mohali, Punjab, schedule an appointment with Dr. Akhil Monga. Take the first step towards stroke prevention and improved blood flow.
Schedule consultation