Fibroids are benign tumors of the uterus (womb). They do not possess cancerous tendencies, so they are not life threatening. Fibroids are highly common and around half of the women in this world get affected with them at some stage of their lives. It is seen that in most of the women with fibroids, symptoms do not even appear at all. They may stay unaware of the presence of fibroids in their body.But some may face huge suffering because of them.Fibroids are made of muscle and are highly vascular i.e. well supplied with blood. Although the causes of fibroid are unknown, the hormones play a huge role in their growth. It is seen that during a woman's mid life when the estrogen levels are at peak, they grow faster. They usually affect the women in the 30-35 years age group and are rarely seen in teenage girls. After the menopause, the fibroids tend to shrink.

Fibroids can be of four types depending on their location.
In most of the cases, fibroids do not interfere with the pregnancy or ability to carry pregnancy. But some of them may lead to an uncomfortable pregnancy. They can even result in difficulty in conceiving or miscarrige in some cases. This is logical as an abnormal lump in the uterus can easily be imagined blocking the fallopian tube preventing the egg travelling from the ovary to the uterus. Pregnancy loss or interference with embryo growth may occur due to the fibroids within the womb lining. Occasionally, few fibroids may become non-vital because of lost blood supply during pregnancy resulting in severe pain, misscarriage or premature delivery.
Large fibroids may obstruct a baby's passage to move out during birth leading to difficult delivery. In such cases, a caesarean section surgery may become necessary. Fibroids may increase the risk of heavy bleeding after birth which may later require some kind of intervention to stop.
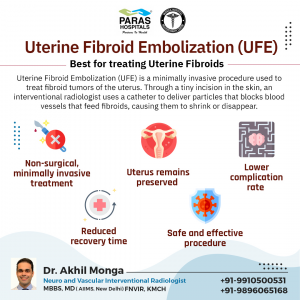
Fibroids have a rich blood supply from the uterine arteries. If these arteries which are supplying the fibroids are blocked, eventually fibroids shrink and symptoms will disappear.
After giving local anesthesia in the hand or leg, through a small pin hole sized access in the artery of the wrist or in the groin, small angiographic catheters are inserted and uterine arteries are entered. Through this small particle called PVA particles are injected which results in shrinkage of the fibroids. This procedure is done inside a cath lab by an interventional radiologist and will only take an average of 45 min €“ 1 hour depending on the anatomy and is particularly effective for fibroids less than 12 cm size.